In the world of engineering and design, the acronyms CAD and CAE are commonly heard. While both are crucial tools, their functions and applications differ significantly. For beginners, understanding CAD vs CAE key differences is essential for mastering the basics of these powerful tools. This blog will provide a detailed yet straightforward comparison, making it easier for newcomers to grasp these concepts.
What is CAD?
CAD, or Computer-Aided Design, is the use of computer technologies to help create, modify, analyze, or optimize a design. CAD software is extensively used in fields such as architecture, engineering, and manufacturing. It allows designers to create precise 2D or 3D models, thus enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of the design process.
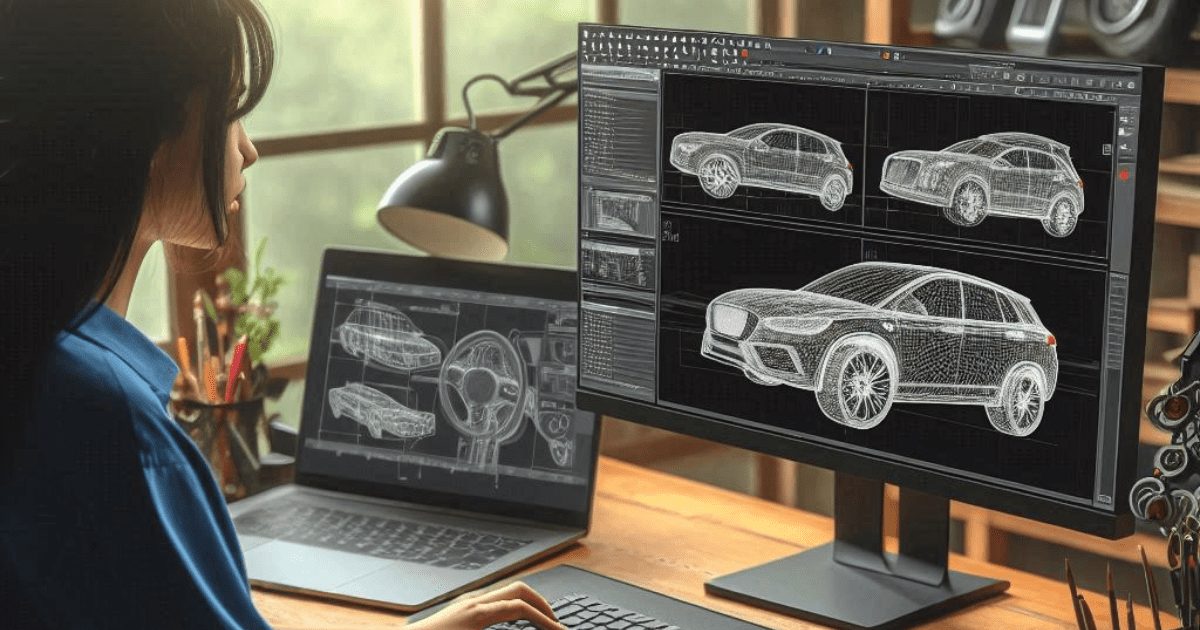
Key Features of CAD:
- 2D and 3D Modeling: CAD software supports both 2D drafting and 3D modeling, enabling the creation of detailed and accurate designs.
- Visualization: Designs can be visualized in three dimensions, helping to identify potential issues early.
- Editing and Modification: Changes to designs can be made easily, enhancing flexibility and reducing the time needed for revisions.
- Documentation: CAD systems generate detailed documentation, including dimensions, materials, and processes, which are essential for manufacturing.
Tools Used for CAD:
Several tools are commonly used for CAD, including:
- AutoCAD: Widely used for a variety of design projects, from architecture to engineering.
- SolidWorks: renowned for its robust 3D modeling features and easy-to-use interface.
- CATIA: Preferred for complex and large-scale design projects.
- Autodesk Inventor: Popular for 3D mechanical design.
- Rhino: Renowned for its precision and flexibility in modeling.
What is CAE?
CAE, or Computer-Aided Engineering, involves the use of computer software to simulate performance, validate designs, and optimize products. CAE encompasses several areas, including Finite Element Analysis (FEA), Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), and multibody dynamics.

Key Features of CAE:
- Simulation: CAE tools simulate how a product will perform under various conditions, such as stress, heat, and fluid flow.
- Analysis: Engineers analyze simulation results to identify potential problems and improve design quality.
- Optimization: Designs are optimized for better performance and efficiency using CAE software.
- Verification: Designs are verified in accordance with industry norms and rules, guaranteeing adherence and security.
Tools Used for CAE:
- ANSYS: Provides comprehensive simulation capabilities across a wide range of applications.
- Abaqus: Commonly employed in Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and multi-body dynamics.
- COMSOL Multiphysics: Known for handling complex simulations involving multiple physical phenomena.
- Siemens NX: Offers a suite of CAE tools for various engineering applications.
- LS-DYNA: Preferred for high-performance simulations, particularly in automotive and aerospace industries.
How CAD Was Done Before the Introduction of Software?
Before CAD software, designs were created manually on paper. Engineers and architects used drafting tables, pencils, compasses, and rulers to create detailed drawings. This method required a significant amount of time and was open to mistakes. Any changes required starting over or making manual corrections, which extended the project duration. The manual drafting method limited the ability to visualize designs in 3D, making it harder to spot potential issues early in the design process.

How CAE Was Done Before the Introduction of Software?
Before CAE software, engineering analysis was performed manually using mathematical equations and physical prototypes. Engineers relied on complex calculations to predict how a design would perform under various conditions. Physical prototypes were built and tested, which was both costly and time-consuming. This manual process limited the ability to quickly test multiple scenarios and optimize designs efficiently. The lack of precise simulations often led to oversights and a longer development cycle.

CAD vs CAE: Key Differences
- Purpose: CAD is primarily used for creating and modifying designs, while CAE focuses on analyzing and optimizing these designs.
- Functionality: CAD supplies instruments for sketching and creating models, whereas CAE provides the ability to simulate and analyze.
- Stage of Design: CAD is used in the initial stages for drafting and visualization, while CAE is used later for validation and optimization.
- Output: CAD outputs detailed design models and drawings, whereas CAE outputs simulation results and performance data.
Conclusion:
CAD and CAE are crucial instruments in the creation and development phase.
CAD is indispensable for creating detailed and precise designs, while CAE is essential for analyzing and optimizing these designs. Understanding the CAD vs CAE key differences helps in utilizing these tools effectively, leading to better design quality and performance.
FAQs:
1.What are the main differences between CAD and CAE?
The main differences lie in their purpose and functionality. CAD is used for creating and modifying designs, while CAE is used for simulating, analyzing, and optimizing these designs.
2.Can CAD and CAE be used together?
Yes, CAD and CAE are often used together. CAD tools are utilized to generate the blueprint, which is subsequently reviewed and enhanced through CAE instruments.
3.What industries benefit most from CAD and CAE?
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, architecture, engineering, and manufacturing benefit significantly from the use of CAD and CAE tools.
4.Is it necessary to learn both CAD and CAE?
Learning both CAD and CAE is beneficial, especially for engineers and designers, as it allows for a comprehensive understanding of the design and analysis process.
5.Are there any free CAD and CAE software available?
Yes, there are free and open-source CAD and CAE software available, such as FreeCAD for CAD and OpenFOAM for CAE.
Understanding the differences and applications of CAD and CAE is essential for anyone involved in design and engineering. With the right knowledge and tools, creating and optimizing high-quality designs becomes more efficient and effective.

